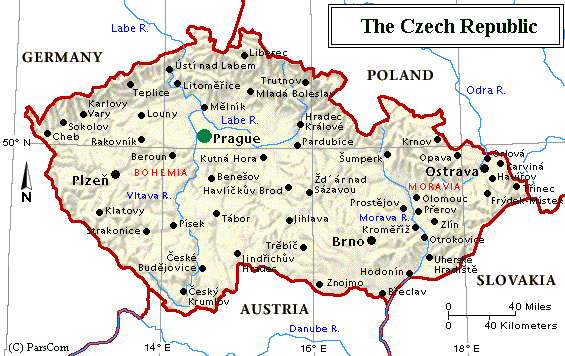

Learn more about the Capital of Czechoslovakia - Prague
Location: Central Europe, southeast of Germany
Map references: Ethnic Groups in Eastern Europe, Europe
Area:
total area: 78,703 sq km
land area: 78,645 sq km
comparative area: slightly smaller than South Carolina
Land boundaries: total 1,880 km, Austria 362 km, Germany 646 km, Poland 658 km, Slovakia 214 km
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
Climate: temperate; cool summers; cold, cloudy, humid winters
Terrain: two main regions: Bohemia in the west, consisting of rolling plains, hills, and plateaus surrounded by low mountains; and Moravia in the east, consisting of very hilly country
Natural resources: hard coal, soft coal, kaolin, clay, graphite
Land use:
arable land: NA%
permanent crops: NA%
meadows and pastures: NA%
forest and woodland: NA%
other: NA%
Irrigated land: NA sq km
Population: 10,432,774 (July 1995 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 19% (female 981,918; male 1,030,003)
15-64 years: 68% (female 3,529,411; male 3,530,112)
65 years and over: 13% (female 848,599; male 512,731) (July 1995 est.)
Population growth rate: 0.26% (1995 est.)
Birth rate: 13.46 births/1,000 population (1995 est.)
Death rate: 10.85 deaths/1,000 population (1995 est.)
Net migration rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1995 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 8.9 deaths/1,000 live births (1995 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 73.54 years
male: 69.87 years
female: 77.41 years (1995 est.)
Total fertility rate: 1.84 children born/woman (1995 est.)
Nationality:
noun: Czech(s)
adjective: Czech
note: 300,000 Slovaks declared themselves Czech citizens in 1994
Ethnic divisions: Czech 94.4%, Slovak 3%, Polish 0.6%, German 0.5%, Gypsy 0.3%, Hungarian 0.2%, other 1%
Religions: atheist 39.8%, Roman Catholic 39.2%, Protestant 4.6%, Orthodox 3%, other 13.4%
Languages: Czech, Slovak
Literacy: can read and write
total population: 99%
Labor force: 5.389 million
by occupation: industry 37.9%, agriculture 8.1%, construction 8.8%, communications and other 45.2% (1990)
Names:
conventional long form: Czech Republic
conventional short form: Czech Republic
local long form: Ceska Republika
local short form: Cechy
Digraph: EZ
Type: parliamentary democracy
Capital: Prague
Administrativedivisions: 8 regions (kraje, kraj - singular); Jihocesky, Jihomoravsky, Praha, Severocesky, Severomoravsky, Stredocesky, Vychodocesky, Zapadocesky
Independence: 1 January 1993 (from Czechoslovakia)
National holiday: National Liberation Day, 9 May; Founding of the Republic, 28 October
Constitution: ratified 16 December 1992; effective 1 January 1993
Legal system: civil law system based on Austro-Hungarian codes; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; legal code modified to bring it in line with Organization on Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) obligations and to expunge Marxist-Leninist legal theory
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Overview: The government of the Czech Republic, using successful stabilization policies to bolster its claims to full membership in the western economic community, has reduced inflation to 10%, kept unemployment at 3%, balanced the budget, run trade surpluses, and reoriented exports to the EU since the breakup of the Czechoslovak federation on 1 January 1993. GDP grew 2% in 1994 after stagnating in 1993 and contracting nearly 20% since 1990. Prague's mass privatization program, including its innovative distribution of ownership shares to Czech citizens via 'coupon vouchers,' has made the most rapid progress in Eastern Europe. When coupon shares are distributed in early 1995, 75%-80% of the economy will be in private hands or partially privatized, according to the Czech government. Privatized companies still face major problems in restructuring; the number of annual bankruptcies quadrupled in 1994. In September 1994, Prague repaid $471 million in IMF loans five years ahead of schedule, making the Czech Republic the first East European country to pay off all IMF debts. Despite these outlays, hard-currency reserves in the banking system totaled more than $8.5 billion in October. Standard & Poor's boosted the Republic's credit rating to BBB+ in mid-1994 - up from a BBB rating that was already two steps higher than Hungary's and one step above Greece's rating. Prague forecasts a balanced budget, at least 3% GDP growth, 5% unemployment, and single-digit inflation for 1995. Inflationary pressures - primarily as a result of foreign bank lending to Czech enterprises but perhaps also due to eased currency convertibility controls - are likely to be the most troublesome issues in 1995. Continuing economic recovery in Western Europe should boost Czech exports and production but a substantial increase in prices could erode the Republic's comparative advantage in low wages and exchange rates. Prague already took steps in 1994 to increase control over banking policies to neutralize the impact of foreign inflows on the money supply. Although Czech unemployment is currently the lowest in Central Europe, it will probably increase 1-2 percentage points in 1995as large state firms go bankrupt or are restructured and service sector growth slows.
National product: GDP - purchasing power parity - $76.5 billion (1994 est.)
National product real growth rate: 2.2% (1994 est.)
National product per capita: $7,350 (1994 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 10.2% (1994 est.)
Unemployment rate: 3.2% (1994 est.)
Budget:
revenues: $14 billion
expenditures: $13.6 billion, including capital expenditures of $NA (1994 est.)
Exports: $13.4 billion (f.o.b., 1994 est.)
commodities: manufactured goods, machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, fuels, minerals, metals, agricultural products (January-November 1994)
partners: Germany 28.7%, Slovakia 15.5%, Austria 7.9%, Italy 6.4%, France 3.2%, Russia 3.2%, Poland 3.1%, UK 2.9%, Netherlands 2.4%, Hungary 2.2%, US 2.1%, Belgium 1.3% (January-June 1994)
Imports: $13.3 billion (f.o.b., 1994 est.)
commodities: machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, chemicals, fuels and lubricants, raw materials, agricultural products (January-November 1994)
partners: Germany 24.1%, Slovakia 15.6%, Russia 9.8%, Austria 7.6%, Italy 4.9%, France 3.6%, US 3.2%, Netherlands 2.9%, UK 2.8%, Poland 2.7%, Switzerland 2.2%, Belgium 2.0% (January-June 1994)
External debt: $8.7 billion (October 1994)
Industrial production: growth rate 4.9% (January-September 1994)
Electricity:
capacity: 14.470,000 kW
production: 56.3 billion kWh
consumption per capita: 4,842 kWh (1993)
Industries: fuels, ferrous metallurgy, machinery and equipment, coal, motor vehicles, glass, armaments
Agriculture: largely self-sufficient in food production; diversified crop and livestock production, including grains, potatoes, sugar beets, hops, fruit, hogs, cattle, and poultry; exporter of forestproducts
Currency: 1 koruna (Kc) = 100 haleru
Fiscal year: calendar year
Railroads:
total: 9,434 km (include 1.520-m broad, 1.435-m standard, and several narrow gauges) (1988)
Highways:
total: 55,890 km (1988)
paved: NA
unpaved: NA
Inland waterways: NA km; the Elbe (Labe) is the principal river
Pipelines: natural gas 5,400 km
Ports: Decin, Prague, Usti nad Labem
Merchant marine:
total:14 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 181,646 GRT/282,296 DWT
ships by type: bulk 5, cargo 9
Airports:
total: 116
with paved runways over 3,047 m: 2
with paved runways 2,438 to 3,047 m: 9
with paved runways 1,524 to 2,437 m: 13
with paved runways under 914 m: 5
with unpaved runways over 3,047 m: 1
with unpaved runways 2,438 to 3,047 m: 3
with unpaved runways 1,524 to 2,438 m: 10
with unpaved runways 914 to 1,523 m: 32
with unpaved runways under 914 m: 41